In the realm of academic writing, an apa format abstract plays a crucial role in conveying the essence of a research paper to potential readers. Whether you are a student, researcher, or academician, understanding the purpose and structure of an abstract is essential for effective communication of your research findings. This blog post aims to shed light on what an abstract is, its significance, and how to craft one according to the American Psychological Association (APA) formatting guidelines.

The Versatility of APA Format in Academic Writing
The American Psychological Association (APA) format has become a staple in academic writing, appreciated for its versatility and applicability across a range of disciplines. While initially designed for psychology-related documents, APA format has evolved into a widely accepted standard for various academic papers. One of the primary domains where APA format finds extensive use is the social sciences, including psychology, sociology, anthropology, and education.
Research articles, literature reviews, and empirical studies in psychology often adhere to the APA guidelines, ensuring uniformity and clarity in presenting research findings. The format’s emphasis on objectivity and precision aligns well with the scientific nature of psychological research.
However, APA format’s influence extends well beyond the confines of psychology. Students and researchers in fields such as nursing, business, communication studies, and education frequently employ APA guidelines for their academic papers. This broad acceptance is due to the format’s adaptability and its ability to provide a standardized structure for diverse types of scholarly documents.
In the realm of education, for instance, APA format is commonly used for research papers, theses, and dissertations. Its standardized approach facilitates effective communication of ideas, allowing educators and students to focus on the content without getting bogged down by inconsistent formatting.
Moreover, APA format is widely favored for literature reviews, where scholars analyze and synthesize existing research on a particular topic. The format’s guidelines for citing sources and organizing information enhance the clarity of literature reviews, contributing to the overall coherence of the academic discourse.
The social sciences, with their emphasis on empirical research and data-driven analysis, benefit significantly from the structure provided by APA format. The inclusion of elements such as abstracts, keywords, and a clear organization of headings enables researchers to present their work in a standardized and easily digestible format.
What is an Abstract?
An abstract is a concise and comprehensive summary of a scholarly article, thesis, dissertation, or any academic paper. Its primary purpose is to provide readers with a brief overview of the research, allowing them to quickly grasp the study’s objectives, methods, results, and conclusions. An effective abstract serves as a standalone document, enabling readers to decide whether the full paper is worth reading.
Key Components of an Abstract:
1. Background and Objectives:
– Briefly introduce the topic and context of the study.
– Clearly state the research question or objective.
2. Methods:
– Outline the research design, methodology, and any statistical procedures used.
– Highlight key aspects of the experimental or investigative approach.
3. Results:
– Summarize the main findings of the study.
– Include essential data and statistical outcomes.
4. Conclusion:
– Present the primary conclusions drawn from the research.
– Highlight the significance and implications of the findings.
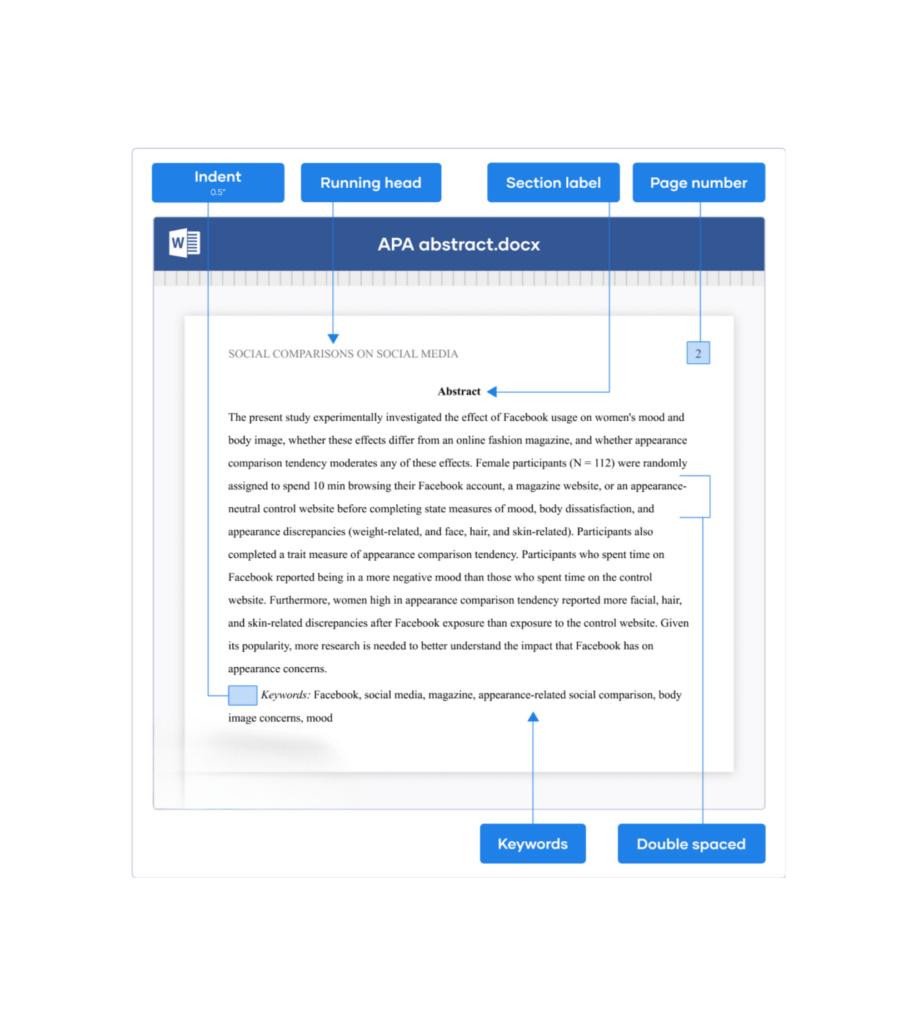
APA Format Abstract:
When it comes to APA formatting, specific guidelines must be followed to structure an abstract properly. Here is a step-by-step guide:
1. Title:
– Begin with the title “Abstract” centered at the top of the page.
– Do not use bold, italics, or underlining.
2. Length:
– Keep the abstract between 150 and 250 words.
– Avoid exceeding this limit, as conciseness is a key principle.
3. Formatting:
– Use a clear, concise, and well-organized paragraph format.
– Double-space the entire abstract.
4. Content:
– Include the research topic, the research question or objective, the methodology, the main results, and the conclusions.
– Avoid citing references or providing detailed background information.
5. Keywords:
– Optionally, include a list of keywords below the abstract.
– Use relevant terms that capture the main themes of the research.
Example of an APA Format Abstract:
In conclusion, crafting an effective abstract is essential for successful scholarly communication. Adhering to APA formatting guidelines ensures consistency and clarity, allowing researchers to convey their findings efficiently. Mastering the art of abstract writing enhances your ability to engage your audience and make a meaningful contribution to the academic discourse.
If including an abstract in your next academic paper seems overwhelming, have no fear. The professional writers at Essay 24 are very well versed in crafting relevant abstracts that comply with APA guidelines. Reach out today to relieve your stress and get your next paper completed within just a few days.