The American Psychological Association (APA) format is a set of guidelines widely used for academic writing in various disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. Developed by the APA, these guidelines ensure consistency and clarity in scholarly communication by providing standards for formatting manuscripts, citing sources, and organizing content. Understanding and adhering to APA format is essential for researchers, students, and professionals to maintain academic integrity and facilitate effective communication of ideas.

Structure of APA Format
APA format encompasses several key elements, including:
1. Title Page: The title page typically includes the title of the paper, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and author note (if applicable). It is formatted in a specific manner, with the title centered in the upper half of the page, followed by the author’s name and institutional affiliation centered beneath it.
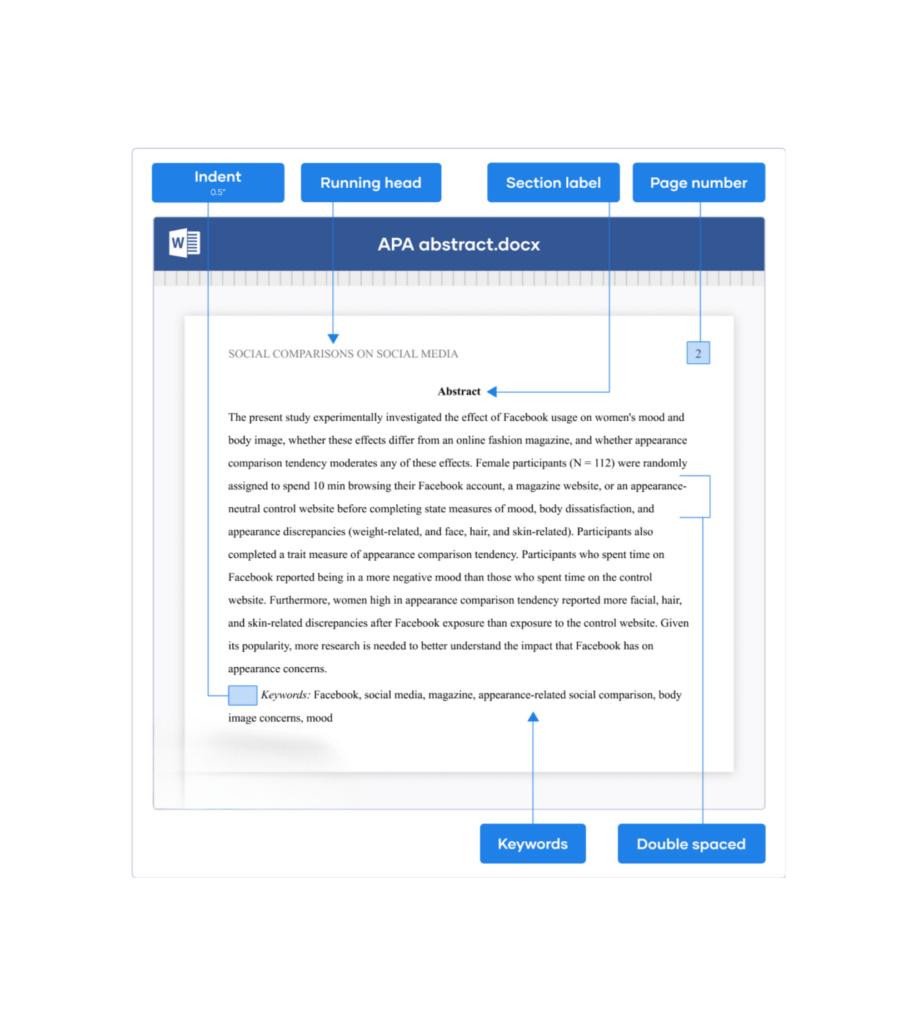
2. Abstract: The abstract is a concise summary of the paper, providing an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions. It is typically between 150 to 250 words and placed on a separate page after the title page.
3. Main Body: The main body of the paper contains the introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections. It is structured logically and divided into distinct sections to present the research coherently.
4. References: The references section lists all the sources cited in the paper. It follows specific formatting guidelines for different types of sources, including books, journal articles, websites, and others.
5. In-text Citations: APA format uses parenthetical in-text citations to acknowledge sources within the text. Citations include the author’s last name and the publication year of the source, such as (Smith, 2019).
6. Headings and Subheadings: Headings and subheadings are used to organize the content and improve readability. APA format specifies five levels of headings, each with its formatting style.
7. Margins, Font, and Spacing: APA format dictates specific requirements for margins, font type (usually Times New Roman), font size (12-point), and line spacing (double-spaced).
Understanding the Significance of APA Running Head in Format
In the realm of academic writing, adherence to formatting guidelines is paramount. It not only ensures professionalism but also aids in the seamless conveyance of ideas. When it comes to the American Psychological Association (APA) format, one such element that holds significance is the running head.
Picture this: You’re flipping through a research paper, scanning its pages to gather information. At the top of each page, you notice a succinct phrase, encapsulating the essence of the paper’s content. This, my friends, is the running head.
The running head is akin to the paper’s identity card, succinctly encapsulating its essence in a few words. It’s a condensed version of the paper’s title, strategically placed atop each page. Think of it as the paper’s beacon, guiding readers through its contents with ease.
In APA format, the running head serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it provides a quick glimpse into the paper’s subject matter, aiding readers in understanding its focus. Secondly, it ensures proper identification of each page, mitigating the risk of disarray should the pages become detached.
Crafting the perfect running head requires precision. It must be concise yet informative, capturing the essence of the paper within a limited character count. Striking this balance is crucial to ensure that the running head effectively serves its purpose without overshadowing the paper’s content.

How to Include APA Running Head in an Academic Paper
Including a running head in an academic paper in APA format involves several steps:
1. Formatting the Running Head: The running head should be flush left at the top of the title page and all subsequent pages. It should be no more than 50 characters in length, including spaces and punctuation. The running head should be in all capital letters and cannot exceed 50 characters, including spaces, punctuation, and letters.
2. Choosing the Content: The content of the running head typically consists of the paper’s title in abbreviated form. It should accurately represent the content of the paper while being concise enough to fit within the character limit.
3. Title Page: On the title page, the running head is preceded by the phrase “Running head:” followed by a colon. The running head itself appears in all capital letters, aligned flush left. It should be positioned in the header area, half an inch from the top margin.
4. Subsequent Pages: On all subsequent pages of the paper, the running head appears in the header area, aligned flush left. However, unlike the title page, the phrase “Running head:” is omitted. Only the abbreviated title is presented.
5. Page Numbers: In addition to the running head, all pages of the paper should include a page number in the header area, aligned flush right. The page number should be preceded by the title of the paper, separated by a space.
6. Formatting Considerations: It is crucial to ensure that the running head is formatted correctly according to APA guidelines. This includes using the appropriate font (usually Times New Roman, 12-point), maintaining the specified character limit, and aligning it correctly within the header area.
7. Proofreading: Before submitting the paper, it is essential to review the running head to verify that it accurately reflects the paper’s title and adheres to APA formatting guidelines. Any errors or discrepancies should be corrected to ensure consistency and professionalism.
In summary, including a running head in an academic paper is a standard requirement in APA format. It serves to provide brief identification of the paper’s content and ensure proper page identification. By following the guidelines outlined above, writers can effectively incorporate a running head into their papers and maintain adherence to APA formatting standards.
Each of the papers crafted by the expert writers at Essay 24 abide by the rules and formatting guidelines set out by your professor. Order your next writing assignment from our online portal, and feel confident that your assignment will be completed to your exact specifications, including APA format rules.